Sanlian Pump Industry Group is a manufacturing enterprise based on water supply and drainage equipment. The group company integrates R&D, design, casting, production and sales, and provides customers with modern, digital and intelligent comprehensive solutions for fluid transportation and integrated systems.
Why Split Case Pumps Remain the Standard for Municipal and Industrial Flow Control
Understanding the Structural Advantage of Split Case Pumps
Split case pumps are engineered with a horizontally split casing that allows direct access to internal components without disturbing piping connections. This design provides a practical advantage in municipal water supply systems and industrial circulation networks where downtime directly impacts operational continuity. The casing is divided along the horizontal centerline, enabling technicians to inspect, maintain, or replace internal components such as the impeller, shaft, and wear rings while the lower half remains anchored to the baseplate.
The double-suction impeller configuration commonly used in split case pumps ensures hydraulic balance by allowing fluid to enter from both sides of the impeller. This reduces axial thrust and enhances bearing life, making these pumps suitable for continuous-duty applications in water treatment plants, cooling water systems, and large-scale irrigation networks. The symmetrical flow path contributes to stable performance even under fluctuating system demands.
Hydraulic Efficiency in Large-Volume Flow Control
Municipal and industrial facilities often require consistent high-volume flow with controlled head pressure. Split case pumps are selected because they provide high hydraulic efficiency across a broad operating range. Their internal geometry minimizes turbulence, which reduces energy loss and supports lower operating costs over long service periods.
Compared with end suction centrifugal pumps, split case pumps generally offer higher flow capacity at lower net positive suction head requirements. This is particularly important in municipal pumping stations where suction conditions may vary depending on reservoir levels. Stable suction performance reduces cavitation risk and prolongs equipment lifespan.
| Feature | Split Case Pumps | End Suction Pumps |
| Flow Capacity | High | Moderate |
| Axial Thrust | Balanced | Higher |
| Maintenance Access | Top Access Design | Full Disassembly Required |
Maintenance Accessibility and Reduced Downtime
One of the primary reasons split case pumps remain widely used in municipal and industrial flow control systems is their service-friendly construction. The top half of the casing can be removed without disconnecting suction and discharge piping. In large facilities where piping networks are rigid and integrated into infrastructure, this design reduces labor intensity and shortens maintenance cycles.
Routine maintenance tasks such as seal replacement, impeller inspection, and bearing servicing can be completed efficiently. This minimizes plant shutdown time and improves overall asset management. For municipal water systems operating around the clock, rapid service capability translates directly into operational reliability.
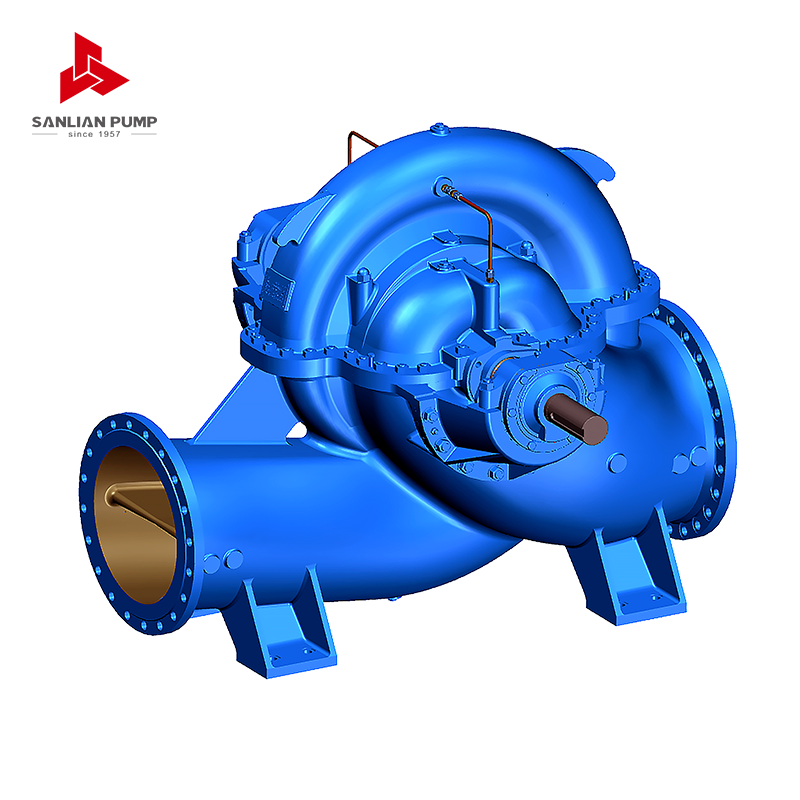
Application Versatility Across Municipal and Industrial Systems
Split case pumps are widely installed in clean water transfer, booster stations, district heating circulation, cooling water systems, and fire protection networks. Their ability to handle large flow volumes with consistent pressure makes them suitable for both low-lift and medium-head applications. Material selections such as cast iron, ductile iron, or stainless steel allow adaptation to different water qualities and system requirements.
- Municipal drinking water distribution systems
- Industrial process water circulation
- HVAC chilled water and condenser water systems
- Flood control and irrigation pumping stations
In industrial facilities where process reliability is critical, split case pumps provide steady hydraulic output even during variable load conditions. Their balanced impeller configuration supports smooth operation under continuous duty cycles.
Mechanical Stability and Long-Term Reliability
Mechanical stability plays a decisive role in long-term flow control performance. The rigid bearing housing and balanced rotor design reduce vibration and mechanical stress. Lower vibration levels protect adjacent equipment and reduce structural fatigue in pump foundations.
The dual-bearing support system maintains shaft alignment and limits deflection under high flow loads. This contributes to extended seal life and consistent hydraulic performance. In municipal infrastructure projects designed for multi-decade operation, such mechanical durability justifies the continued preference for split case pumps.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Cost Control
Energy consumption represents a significant portion of operating costs in water transport systems. Split case pumps typically operate near peak efficiency across a broad flow range. When paired with variable frequency drives, they allow precise control of flow rates without substantial efficiency penalties.
Lower hydraulic losses and reduced mechanical wear translate into measurable lifecycle savings. Municipalities and industrial operators prioritize equipment that supports stable performance with predictable maintenance intervals, and split case pumps consistently meet these operational expectations.
Why Split Case Pumps Continue to Lead Flow Control Systems
The continued dominance of split case pumps in municipal and industrial flow control applications is not based on tradition alone. Their structural accessibility, hydraulic efficiency, balanced mechanical design, and adaptability to high-volume systems make them a dependable solution for large-scale fluid transport. In environments where uninterrupted operation and energy efficiency are critical, these pumps maintain their position as a preferred engineering choice.
As infrastructure modernization projects expand globally, split case pumps remain central to water management strategies. Their proven performance in demanding flow control scenarios confirms why they are still regarded as the industry standard.








 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى




 皖公网安备34052302341647号
皖公网安备34052302341647号