Sanlian Pump Industry Group is a manufacturing enterprise based on water supply and drainage equipment. The group company integrates R&D, design, casting, production and sales, and provides customers with modern, digital and intelligent comprehensive solutions for fluid transportation and integrated systems.
How Does an Abrasion Resisting Pump Reduce Wear in Slurry Applications
Understanding Wear Mechanisms in Slurry Pumping
In slurry applications, pumps are required to handle fluids containing solid particles such as sand, ore, ash, or tailings. These particles cause continuous mechanical interaction with internal pump surfaces, leading to abrasive wear, erosion, and surface fatigue. Wear typically concentrates in high-velocity zones such as impellers, volutes, liners, and seal areas. If not properly managed, this wear results in efficiency loss, leakage, frequent maintenance, and shortened equipment life.
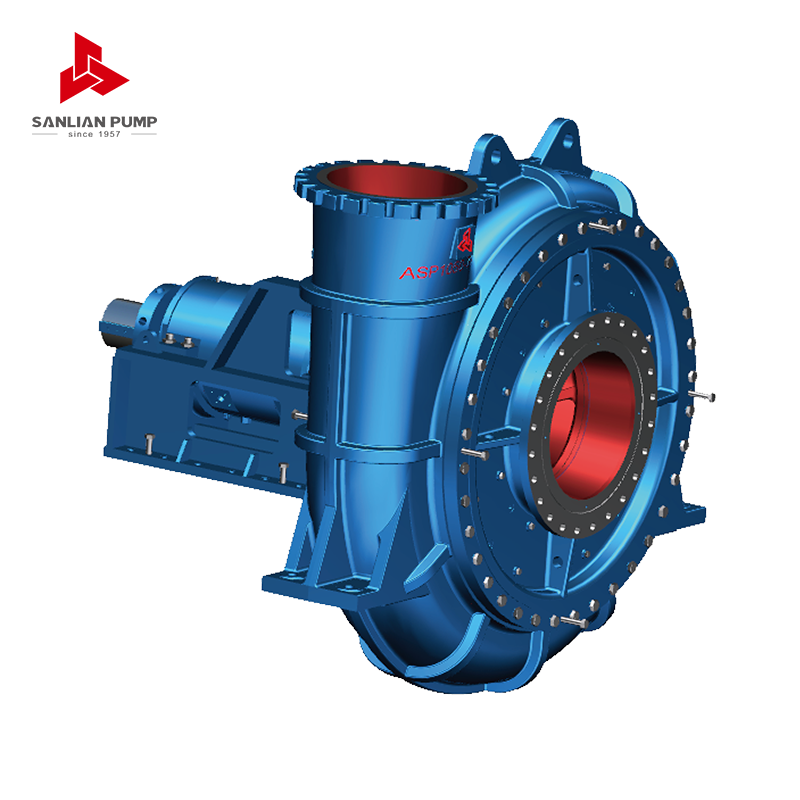
Material Selection as the First Line of Wear Reduction
Abrasion resisting pumps reduce wear primarily through the use of specialized materials designed to withstand continuous particle impact. Unlike standard pumps, these pumps use wear-resistant alloys, rubber linings, or composite materials that maintain surface integrity under abrasive conditions. The hardness, elasticity, and microstructure of these materials play a direct role in slowing material loss and maintaining dimensional stability during long-term operation.
Common Wear-Resistant Material Characteristics
- High surface hardness to resist cutting and gouging by sharp particles
- Elastic properties that absorb particle impact and reduce surface cracking
- Chemical stability to prevent corrosion-assisted abrasion
Optimized Hydraulic Design to Control Particle Flow
Beyond material selection, abrasion resisting pumps reduce wear through hydraulic designs that manage how slurry flows through the pump. Smooth flow paths, reduced turbulence, and controlled velocity distribution limit the intensity of particle collisions with internal surfaces. By minimizing sharp directional changes and dead zones, the pump reduces localized erosion and uneven wear patterns.
Design Features That Lower Abrasive Impact
- Enlarged flow passages to lower particle velocity
- Gradual curvature in volutes and casings to reduce turbulence
- Impeller profiles designed for uniform slurry acceleration
Replaceable Wear Components and Modular Construction
Abrasion resisting pumps are typically designed with replaceable wear components such as liners, impellers, and throat bushings. Instead of allowing wear to affect the pump casing or shaft, these components absorb the majority of abrasive damage. When wear reaches a defined limit, only the affected parts are replaced, preserving the core structure of the pump and reducing maintenance costs.
Maintaining Performance Stability Over Time
As wear progresses in conventional pumps, internal clearances increase, leading to efficiency loss and unstable operation. Abrasion resisting pumps slow this progression by maintaining surface geometry for longer periods. Stable clearances help preserve flow rate, pressure, and energy efficiency, which is critical in continuous slurry transport systems where performance fluctuations can disrupt downstream processes.
Why Abrasion Resisting Pumps Are Effective in Slurry Applications
Abrasion resisting pumps reduce wear in slurry applications through a combination of durable materials, controlled hydraulic design, and replaceable wear components. Rather than eliminating abrasion entirely, these pumps manage and slow the wear process in a predictable way. This approach supports longer service intervals, lower maintenance frequency, and more reliable operation in environments where abrasive solids are unavoidable.








 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى




 皖公网安备34052302341647号
皖公网安备34052302341647号