Sanlian Pump Industry Group is a manufacturing enterprise based on water supply and drainage equipment. The group company integrates R&D, design, casting, production and sales, and provides customers with modern, digital and intelligent comprehensive solutions for fluid transportation and integrated systems.
Industrial Split Case Pumps for High-Flow and Continuous-Duty Applications
Operating Demands in High-Flow and Continuous-Duty Pumping Systems
Industrial pumping systems designed for high-flow and continuous-duty operation place consistent mechanical and hydraulic stress on equipment. These systems typically run for extended periods with limited shutdown windows, handling large volumes of water or process fluids under stable yet demanding conditions. Flow rates are often sustained rather than intermittent, and any instability can directly affect downstream equipment, system pressure balance, and overall operational efficiency.
In such environments, pump selection is driven by structural balance, hydraulic efficiency at high flow, ease of maintenance, and long-term operational stability. Split case pumps are widely specified for these conditions due to their inherent mechanical symmetry and suitability for large-capacity applications.
Structural Characteristics of Industrial Split Case Pumps
Industrial split case pumps feature a horizontally split casing that allows the upper half of the casing to be removed without disturbing the suction and discharge piping. This configuration supports precise internal alignment while simplifying inspection and servicing. For high-flow systems, the casing geometry is designed to accommodate large impeller diameters and wide flow passages, minimizing hydraulic losses.
The split casing structure also improves load distribution across the pump body. Under continuous-duty operation, this balanced structure reduces casing deformation and maintains stable internal clearances, which is critical for sustaining consistent performance over long service cycles.
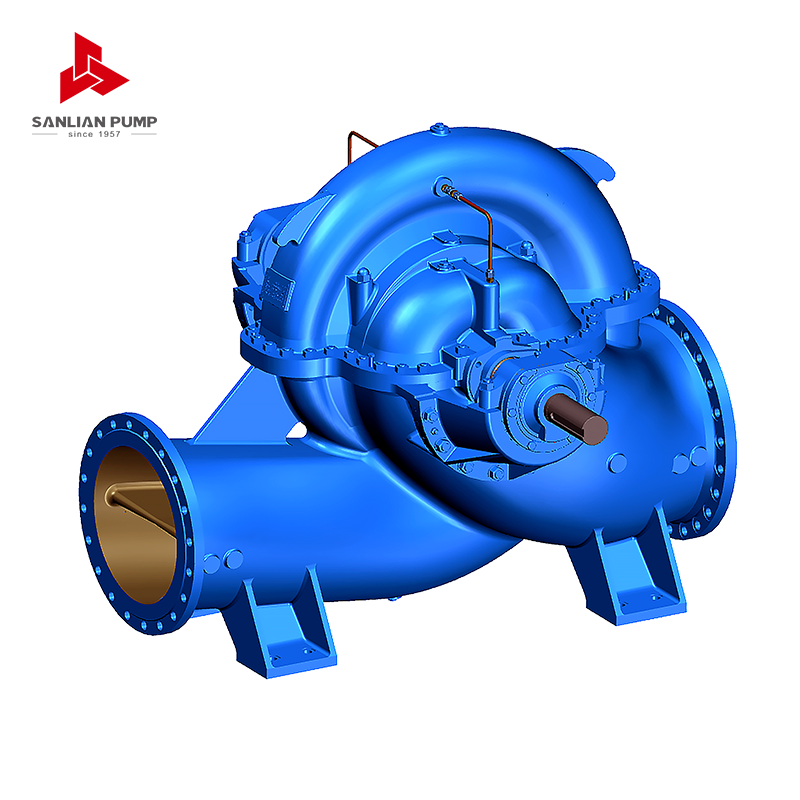
Double Suction Design and Hydraulic Balance
Most industrial split case pumps used in high-flow applications adopt a double suction impeller design. Fluid enters the impeller from both sides, which significantly reduces axial thrust during operation. This hydraulic balance lowers bearing load and shaft deflection, contributing to smoother operation and extended component life.
By distributing flow evenly across the impeller, double suction designs also enhance suction performance and reduce the risk of cavitation in large-volume systems. This characteristic is particularly important in installations with limited net positive suction head available.
Suitability for Continuous-Duty Industrial Operation
Continuous-duty operation requires pumps to maintain stable performance without excessive vibration, heat buildup, or efficiency degradation. Industrial split case pumps are commonly selected for these conditions due to their rigid shaft design, symmetrical casing, and robust bearing arrangements. These features support long operating hours while maintaining consistent hydraulic output.
In systems where downtime directly impacts production or facility operation, the ability of split case pumps to operate reliably under constant load becomes a key engineering consideration rather than an optional feature.
Maintenance Accessibility and Service Efficiency
Maintenance planning is a critical aspect of continuous-duty pump installations. The horizontal split casing allows internal components such as the impeller, shaft, bearings, and wear rings to be accessed without removing the pump from the pipeline. This design reduces service time and limits disruption to connected systems.
For industrial facilities operating under tight maintenance schedules, this accessibility supports predictive maintenance strategies and helps reduce total lifecycle service costs.
- Upper casing removal without disturbing pipe alignment
- Simplified inspection of hydraulic and rotating components
- Reduced maintenance downtime in continuous operation systems
Application Scenarios Requiring High Flow and Long Operating Hours
Industrial split case pumps are commonly applied in systems where large volumes of fluid must be transferred reliably over extended periods. These applications often involve stable operating points rather than frequent flow variation, making hydraulic efficiency at rated conditions a primary concern.
- Power plant cooling water circulation systems
- Steel and metallurgical process water supply
- District cooling and large HVAC central plants
- Municipal and industrial water transfer stations
Key Engineering Parameters for System Integration
When integrating industrial split case pumps into high-flow systems, engineers focus on parameters that directly affect operational stability. These include shaft diameter relative to power transmission, bearing selection for continuous load, casing pressure rating, and alignment tolerance. Each factor contributes to the pump’s ability to operate without excessive wear or performance fluctuation.
Attention to these details during the design and specification phase helps align pump characteristics with system requirements, reducing the risk of premature failure or efficiency loss.
Comparison with Other Pump Configurations in High-Flow Systems
| Design Aspect | Split Case Pumps | End Suction Pumps |
| Typical Flow Capacity | High to very high | Low to medium |
| Axial Thrust Control | Hydraulically balanced | Single-sided load |
| Maintenance Access | Internal access without pipe removal | Pump removal often required |
Long-Term Reliability in Industrial Pumping Environments
For industrial operators, long-term reliability is a result of both design integrity and proper system matching. Split case pumps, when correctly specified and installed, provide stable hydraulic performance, predictable maintenance intervals, and consistent efficiency over extended operating periods.
In high-flow and continuous-duty applications, these characteristics make industrial split case pumps a practical and widely adopted solution for maintaining uninterrupted fluid transport in demanding operating environments.








 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى




 皖公网安备34052302341647号
皖公网安备34052302341647号