Sanlian Pump Industry Group is a manufacturing enterprise based on water supply and drainage equipment. The group company integrates R&D, design, casting, production and sales, and provides customers with modern, digital and intelligent comprehensive solutions for fluid transportation and integrated systems.
Ultimate Slurry Pump Guide: Types, Applications, and Selection Tips
Understanding Slurry Pumps
Slurry pumps are specialized devices designed to handle abrasive, corrosive, and high-density mixtures of solids and liquids. These pumps are widely used in industries such as mining, metallurgy, chemical processing, and power generation. The ability to efficiently transport slurries without excessive wear or energy loss is essential for operational reliability and cost management.
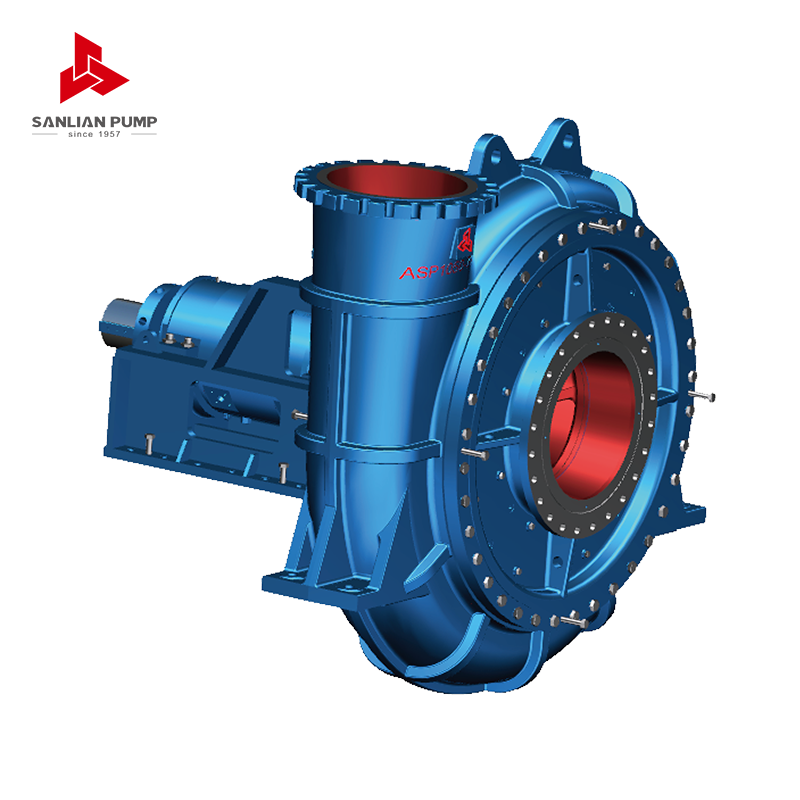
Types of Slurry Pumps
Slurry pumps can be categorized based on their design, material, and application. Understanding the types is crucial for selecting the right pump for specific industrial needs.
Centrifugal Slurry Pumps
Centrifugal slurry pumps are the most common type. They use a rotating impeller to transfer energy from the motor to the slurry, producing high flow rates and moderate pressure. They are ideal for transporting large volumes of low- to medium-density slurries.
Piston or Diaphragm Pumps
These pumps operate with reciprocating motion, providing high pressure for moving slurries over long distances. They are suitable for highly abrasive or high-density slurries that are challenging for centrifugal pumps.
Submersible Slurry Pumps
Submersible slurry pumps are designed to be fully submerged in slurry tanks or sumps. They reduce the need for priming and are effective for dredging or slurry extraction applications in confined spaces.
Applications of Slurry Pumps
Slurry pumps serve a wide range of industrial applications. Their ability to handle abrasive and corrosive materials makes them indispensable in sectors where slurry transport is critical.
- Mining: Transporting ore slurries from mines to processing plants.
- Metallurgy: Moving metal concentrates and tailings efficiently.
- Chemical Industry: Handling acidic or corrosive slurries in chemical processes.
- Power Generation: Pumping ash slurries and cooling water mixtures.
- Construction: Transporting cement, sand, or other slurry-based materials.
Key Components and Materials
Slurry pumps are subject to extreme wear and corrosion. Selecting the right materials for key components is critical to maximize lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
Impeller
Impellers are often made of high-chrome alloy or rubber-lined materials. High-chrome alloys are preferred for abrasive slurries, while rubber linings are suitable for mildly abrasive, corrosive slurries.
Pump Casing
Pump casings protect the pump structure from wear. Materials range from cast iron to stainless steel or polyurethane, depending on the slurry’s abrasiveness and chemical properties.
Shaft and Bearings
Shafts must be strong enough to withstand torque and bending, often made from alloy steel or stainless steel. Bearings are selected based on load and slurry exposure, and proper lubrication is essential for longevity.
Selection Guidelines for Slurry Pumps
Choosing the right slurry pump involves evaluating several operational and technical factors. Proper selection ensures efficiency, minimizes downtime, and reduces total operational costs.
Flow Rate and Head
Calculate the required flow rate and discharge head based on the specific process. Underestimating these parameters may lead to insufficient transport, while overestimating can cause energy inefficiency and wear.
Slurry Density and Particle Size
High-density slurries with large particles require pumps with abrasion-resistant materials and robust impeller design. Consider both weight percentage and particle size distribution when selecting a pump.
Material Compatibility
Ensure that all wet-end materials are resistant to chemical corrosion and abrasion specific to the slurry. Misalignment between material choice and slurry composition can result in rapid wear and pump failure.
Maintenance and Accessibility
Select pumps that allow easy access for inspection, maintenance, and replacement of wear parts. Modular designs with replaceable liners or impellers simplify servicing and reduce downtime.
Comparative Overview of Slurry Pump Types
| Pump Type | Best Suited For | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal | Low to medium-density slurries | High flow rate, simple design, easy maintenance | Moderate wear resistance, not ideal for very dense slurries |
| Piston/Diaphragm | High-density, abrasive slurries | Handles high pressure, suitable for long-distance transport | Lower flow rates, complex design |
| Submersible | Extraction and dredging applications | No priming needed, compact installation | Limited to submerged applications, maintenance can be challenging |
Conclusion
Selecting the right slurry pump requires careful evaluation of the slurry characteristics, operational conditions, and material compatibility. By understanding the types, applications, and key components, industrial operators can maximize efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and extend pump lifespan. Proper selection and maintenance are essential for achieving reliable slurry transport in demanding industrial environments.








 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Français
Français Español
Español Português
Português عربى
عربى




 皖公网安备34052302341647号
皖公网安备34052302341647号